Traditional Public Administration (TPA): Famous 5 Paradigms
Today, we try to discuss the paradigm of Traditional Public Administration (TPA). Next, we will discuss the Modern Public Administration Paradigms. This writing doesn’t deliver the details. But, here will touch on the main point of the topic. However, let’s start the review of the paradigms of traditional public administration. For instance:-
What is Traditional Public Administration (TPA)?
Traditional Public Administration (TPA) is a concept that is limited to a specific characteristic. For example, established an administration under the formal control of the political leadership, strictly decorated with the hierarchical theory of bureaucracy, based on neutral, and permanent staff, motivated by public interest, served equally to any government party, and so on. It has some particular approaches. The main approaches are included below. Such as-
- Legal Approach: Emphasizes strict adherence to laws and regulations, prioritizing formal rules and procedures in public administration.
- Scientific Approach: Grounded in scientific management principles, seeks efficiency and productivity through systematic processes in administrative functions.
- An Institutional and Structural Approach: Focuses on the organizational structure and institutions, examining how administrative bodies are organized and operate.
- Historical Approach: Analyzes public administration’s historical evolution, considering the impact of past events on administrative practices.
- Consensus Approach: Highlights the importance of consensus-building in decision-making, promoting cooperation among stakeholders for effective governance.
- Case Method Approach: Studies specific cases to derive general principles, emphasizing practical experiences and real-world situations.
- Behavioral Approach: Examines the behavior of individuals and groups within administration, considering psychological and social factors influencing administrative actions.
These approaches provide different perspectives for understanding and studying Traditional Public Administration, reflecting diverse aspects ranging from legal considerations to behavioral dynamics.

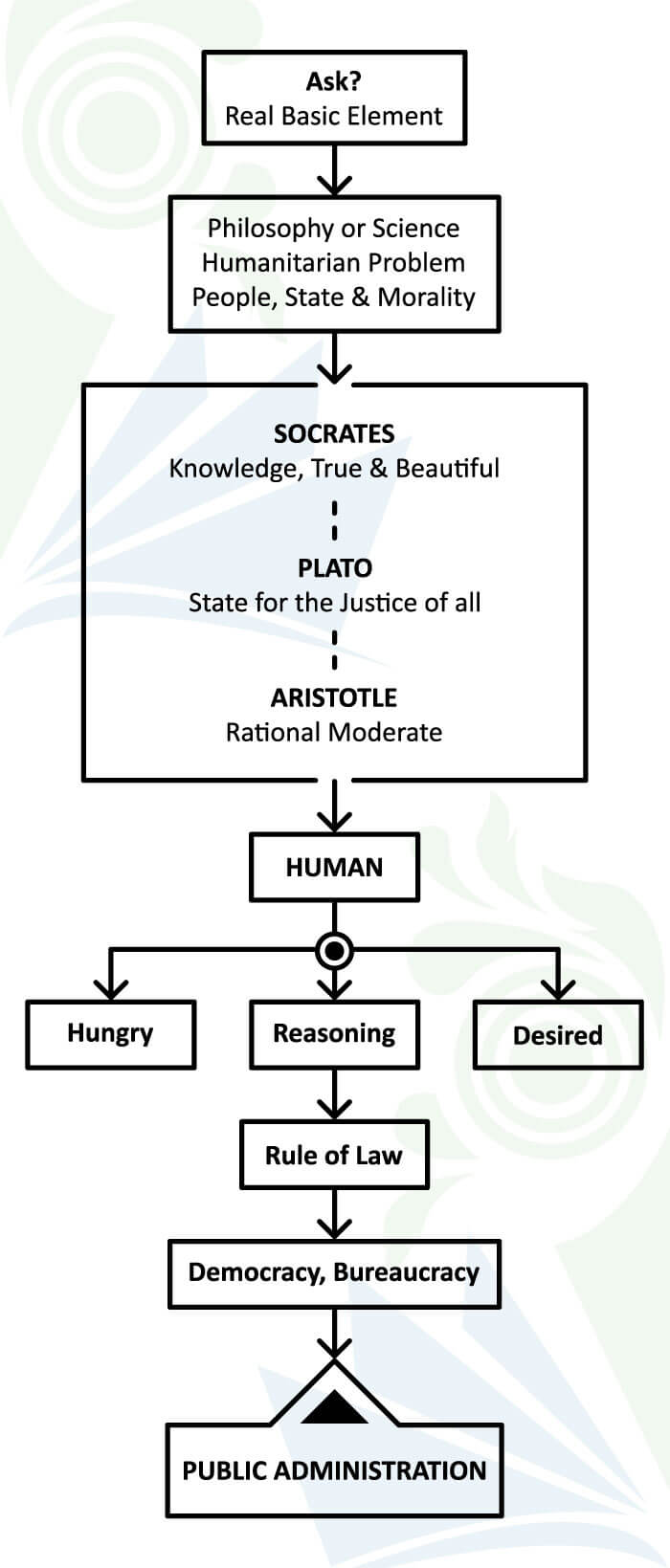
Paradigms of Public Administration
In theory and practice, Traditional Public Administration (TPA) began in the late 20th century. It lasted in Western countries up to the last quarter of the 20th century. The beginning of the TPA model is best seen in the mid-19th century in Britain. After all, the Paradigms of Traditional Public Administration (TPA) are five. Such as:-
- Politics/Administrative Dichotomy,
- Principles of Administration,
- Political Science (Public Administration as Political Science),
- Management (Public Administration as Management), and
- Public Administration as Public Administration.

1. Politics/Administrative Dichotomy (1900-1926)
Firstly is the politics or administration dichotomy. Formerly, US President Woodrow Wilson published the book “The Study of Administration (1887)”. From this book arose the dichotomy between politics and administration. He inserted two activities of the state there. Such as:-
- Politics activities
- Administration activities
About the administration didn’t detail from him. But its thinking accepted two administrators. They were Frank J. Goodnow and L. D. White. They shared two different opinions. Such as:-
Frank J. Goodnow:
Frank J. Goodnow published a book “Politics and Administration (1900)”. In that, his opinions are two. For instance:- politics is a policy of the state. Another, the administration is the implementation of state policy.
L. D. White:
L. D. White published a book “Introduction to the Study of Public Administration (1939)”. It is the first book in the field of public administration. He said a single thing, in that matter. For instance:- politics is apart from the administration.
2. Principles of Administration (1927-1937)
Secondly, it is the principles of administration. W. F. Willoughby published the book “Principles of Administration (1927)”. In this session, contributed many administrators. Along with this, they tried to develop the principles of administration. Mary Parker Follett, Henri Fayol, James Mooney, and Alan Reiley highlighted the self. For instance:-
| Author | Book | Published |
|---|---|---|
| Frederick Winslow Taylor | Scientific Management | 1911 |
| Mary Parker Follett | Creative Experience | 1924 |
| James Mooney & Alan Reiley | Principles of Organization | 1947 |
| Henri Fayol | General and Industrial Management | 1949 |
Luther Gulick and Lyndall Urwick published the book “Papers on the Science of Administration (1937)”. Here built in the POSDCORB. It is an ideal principle of public administration. Such as:-
- P = Planning,
- O = Organizing,
- S = Staffing,
- D = Directing,
- CO = Cooperating,
- R = Regulating, and
- B = Budgeting.
Nevertheless, you can check the Steps of POSDCORB. This article carries the value of practical examples. And, also includes the essential things.
3. Political Science; Public Administration as Political Science (1950-1970)
Thirdly, is Public administration a political science? Here, TPA earned the second status of political science. As a result, the public administration lost its height. And stamped out the importance of making a separate field or subject.
4. Management; Public Administration as Management (1956-1970)
Fourthly is public administration as management. Public administration has turned down the bias of the 2nd status of political science. The public administration, as the proclamation of control, code, there.
Although public administration was born from political science, it passed childhood life in management to reach youth life.
5. Public Administration as Public Administration (1971-till now)
Fifthly is Public administration as general administration. It is the final paradigm of Traditional Public Administration. Here public administration occupies its core status as a separate study.
NAPAA (National Association of Public Affairs and Administration) is an international institute. It has helped to reach the TPA status, although many limitations are covered there. NAPAA is the generator Institute of TPA.
This writing reviews the paradigms of public administration.
Finally, we can able to determine the paradigms. After reading this article, a student can enrich his learning in this field. This article is not only for the student but also for any inheritors of public administration. The development of private and public administration is another relevant article. Anybody should read it, after all.
Paradigms or evaluations of public administration are an important topic in this study. Without the proper knowledge, you can’t complete the actual studies. So, you have to read it. In reading, the following books may help you properly.


Tradition Public Administration (TPA) Paradigms is a very important discussion for administrative students; specially for public administration students. Thanks for sharing it.
Williams Jonh thanks for attaching your opinion. Keep touching our this official HigherStudy.org website to get more valuable articles that may be more important to you.
Many thanks for this article. I’d also like to express that it can possibly be hard if you find yourself in school and merely starting out to establish a long credit standing. There are many students who are simply just trying to make it and have an extended or good credit history can often be a difficult thing to have. voice-vision.de
I had a lack of knowledge about the paradigms of public administration. Your this valuable article help me extremely. Thank you!
I want to know more traditional Public Administration (TPA) Paradigms
Like!! I blog quite often and I genuinely thank you for your information. The article has truly piqued my interest.
I am genuinely thankful to the owner of this site who has shared this great post at at this time.