The Emergence of Public Administration as a Discipline: A Comprehensive Analysis
The field of public administration has evolved significantly over the past centuries, emerging as a distinct academic discipline in response to numerous socio-political, economic, and administrative challenges. For students and scholars, understanding the historical and contextual factors that led to the establishment of public administration provides valuable insights into its current practices and future directions. This article explores the key causes behind the emergence of public administration, emphasizing its relevance and development over time.
Table of Contents
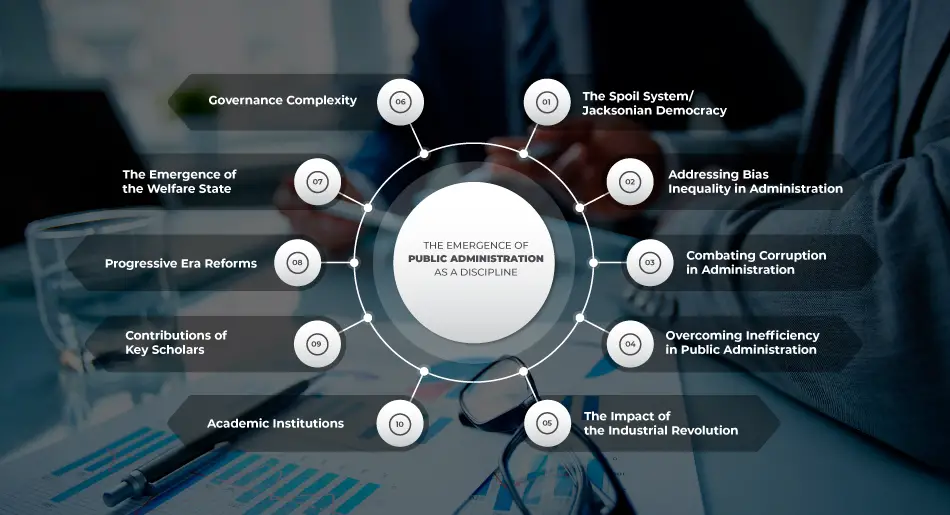
Causes of Emergence of Public Administration as A Discipline
The emergence of public administration as a distinct discipline can be attributed to a variety of factors, ranging from socio-political changes to academic developments. Here are the primary causes:
- The Spoil System and Jacksonian Democracy in the USA
- Addressing Bias and Inequality in Administration
- Combating Corruption in Administration
- Overcoming Inefficiency in Public Administration
- The Impact of the Industrial Revolution
- The Emergence of the Welfare State
- Progressive Era Reforms
- Contributions of Key Scholars and Academic Institutions
- Complexity of Governance
1. The Spoil System and Jacksonian Democracy in the USA
The Spoil System, closely associated with President Andrew Jackson’s administration (1829-1837), played a pivotal role in the early development of public administration. Jacksonian Democracy promoted the idea of rotating officeholders, resulting in the appointment of political loyalists to government positions regardless of their qualifications. This practice led to widespread inefficiency and corruption within the public sector.
The resultant administrative chaos and public dissatisfaction highlighted the need for a more professional and merit-based administrative system. The Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act of 1883 marked a significant shift towards such a system, introducing competitive exams and merit-based appointments. This reform was a crucial step in establishing the foundations for modern public administration.
2. Addressing Bias and Inequality in Administration
Bias and favoritism in administrative practices created significant disparities in public service delivery. Such inequities undermined public trust and efficiency, necessitating the development of a more equitable and standardized approach to administration. Reforms aimed at eliminating bias emphasized fairness, impartiality, and adherence to professional standards.
Efforts to address these issues led to the establishment of policies and practices designed to ensure equal treatment and transparency in public administration. These reforms were instrumental in shaping the field into one that values justice and efficiency, further highlighting the need for a disciplined and systematic approach to governance.
3. Combating Corruption in Administration
Corruption has historically been a significant obstacle in public administration, eroding public trust and impeding effective governance. The prevalence of corrupt practices underscored the urgent need for systematic reforms and the development of a professional body of knowledge to combat these issues.
Efforts to eliminate corruption included the establishment of ethical standards, accountability mechanisms, and transparency measures. These initiatives were crucial in promoting integrity and efficiency in public administration, reinforcing the importance of a professional and disciplined approach to managing public affairs.
4. Overcoming Inefficiency in Public Administration
Inefficiency in administrative practices led to suboptimal public service delivery and resource management. This inefficiency highlighted the necessity for a more systematic approach to governance. The drive to improve productivity, effectiveness, and efficiency in public administration spurred the adoption of scientific management principles.
Frederick Taylor’s principles of scientific management, which advocated for the systematic study and optimization of work processes, had a profound impact on public administration. This movement towards a more organized and efficient approach to administration underscored the importance of developing specialized knowledge and skills in the field.
5. The Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution brought about profound socio-economic changes, including urbanization, increased population density, and more complex societal needs. These changes demanded efficient public administration to manage issues such as public health, infrastructure, and social services.
The complexity of these new administrative challenges spurred the development of public administration as a discipline focused on systematically addressing these needs. The rise of industrialization underscored the necessity for a professional and well-organized public administration capable of managing the growing demands of urban and industrial societies.
6. The Emergence of the Welfare State
The emergence of the welfare state in the 20th century expanded the role of government in providing social services and ensuring the well-being of citizens. This expansion required specialized knowledge and skills to administer programs effectively, manage public resources, and implement policies.
The welfare state’s demands for efficient and effective administration further solidified the importance of public administration as a distinct academic and professional field. The need to develop and implement social policies, manage public resources, and ensure the delivery of essential services emphasized the critical role of public administration in modern governance.
7. Progressive Era Reforms
The Progressive Era (1890s-1920s) in the United States saw a push for reforms aimed at reducing corruption and increasing efficiency in government. Reformers sought to professionalize the public service, reduce the influence of political machines, and introduce scientific management principles. These reforms underscored the need for a systematic approach to public administration, laying the groundwork for the field’s development.
8. Contributions of Key Scholars and Academic Institutions
The formalization of public administration as an academic discipline was significantly influenced by scholars such as Woodrow Wilson (who is known as the father of public administration). Wilson’s seminal essay “The Study of Administration” (1887) advocated for the separation of politics and administration, emphasizing the need for a professional bureaucracy. The establishment of academic programs and institutions dedicated to public administration further cemented its status as a distinct field of study.
9. Complexity of Governance
As societies have grown more complex, the need for structured and efficient governance systems has increased. This complexity demands specialized knowledge and skills to manage public affairs effectively, which has driven the development of public administration as a distinct field of study.
Conclusion
The emergence of public administration as a distinct discipline is a response to various historical, social, and economic challenges. Factors such as the Spoil System and Jacksonian Democracy, bias and inequality, corruption, inefficiency, the Industrial Revolution, the rise of the welfare state, Progressive Era reforms, and contributions from key scholars all played significant roles in highlighting the need for a systematic and professional approach to public administration.
Understanding these causes provides valuable insights into the development and evolution of public administration. For students and scholars, this knowledge is essential in appreciating the complexities and importance of public administration in contemporary governance. As the field continues to evolve, the lessons from its emergence remain relevant, guiding future developments and reforms in public administration.