Who Is the Father of Public Administration and Why?
Public administration refers to the implementation of public policy, the administrative management of government institutions and non-profit organizations, and also the academic discipline that studies these activities and prepares civil servants for working in the government and nonprofit sector. Public administrators are responsible for making sure that the policies set by elected officials or board members are carried out effectively and efficiently. They must also be able to think critically and creatively, solve problems, and communicate effectively with others.
Antiquity Era or When was public administration founded?
Public administration is an ancient practice that dates back to the 8th and 7th centuries BC. This period is commonly known as the Antiquity Era, and it was during this time that kings, pharaohs, and emperors ruling ancient Greece chose citizens to act as their “eyes and ears” for public affairs. These liaisons were responsible for relaying important news and updates from the government to the people, and they also served as representatives of the populace in meetings with officials. Over time, the role of the public administrator has evolved to include a wider range of responsibilities such as overseeing public policy, managing government agencies, and implementing legislation.

Who wrote the first public administration?
The first textbook to be published about public administration was Leonard White’s Introduction to the Study of Public Administration in 1926. This pioneering work explored the field and helped to establish it as a legitimate academic discipline. White himself was one of the pioneers of public administration, having served as the first head of the United States Civil Service Commission.
Who is the father of public administration and why?
Woodrow Wilson is one of the most important figures in the history of public administration. He was the first president to appoint a cabinet-level official dedicated to overseeing the government bureaucracy, and he helped develop the concept of the administrative state. Wilson also wrote extensively on the subject of public administration, and his work continues to be influential to this day.
Woodrow Wilson is considered the father of public administration, as he was one of the first to recognize and study this field as an academic discipline. Wilson’s book “The Study of Administration” helped to define the parameters of what administrative work entails. He also served as the president of the United States from 1913 to 1921, during which time he championed the idea of self-government at the national level.
He contributed significantly to the development of administration as both a science and an academic study. Wilson emphasized the need for administrators to make decisions based on a clear understanding of potential policies and their effects. In addition, he helped to create the first professional school of public administration at Harvard University.
Who is the thinker of new public administration?
The two books “Towards a New Public Administration: The Minnowbrook Perspective” edited by Frank Marini and published in 1971, and “Public Administration in a Time of Turbulence” edited by Dwight Waldo. The concept of New Public Administration was first put forth by Waldo in 1938. He argued that the traditional model of bureaucracy was no longer effective in governing the complexities of the modern world. In his book, Waldo proposed a new model of government administration that would be more responsive to the needs of the people. His ideas were influential in shaping the course of public administration in later years. This new perspective called for changes in the way public agencies operate, with an emphasis on greater openness, accountability, and participation by citizens and interest groups. It also called for improved managerial practices and the use of technology. The New Public Administration movement affected how public administrators think about their work and how they interact with the public.
Who is the father of public administration in India?
Paul H. Appleby was one of the foremost scholars on public administration in India. He is credited with helping to found the discipline in India, and his work has been highly influential in shaping modern thinking on the subject. Appleby’s seminal work, The Theory of Public Administration, laid the foundation for our understanding of the field. In it, he articulated a theory of governance that took into account both the limitations of the individual and the need for an effective civil service. Appleby’s work has been recognized by scholars around the world, and he is considered one of the fathers of public administration.
Paul H. Appleby was a highly respected Indian administrator and thinker whose work is still quoted regularly today. Appleby’s seminal 1948 text, “Principles of Public Administration“, is considered a classic in the field and has been translated into many languages. In it, he proposed an enduring model for public administration that drew on both Western and Indian thinking. Appleby’s ideas have been enormously influential in shaping modern government practices around the world.
Final Words
Public administration is a field of study that has been around for centuries. The father of public administration is considered to be Woodrow Wilson, although Frank Marini and other scholars have made important contributions as well. Paul H. Appleby has similarly measured a father of public administration in India. Contrary to what some people believe, public administration is not a new concept – it has been around since ancient times.
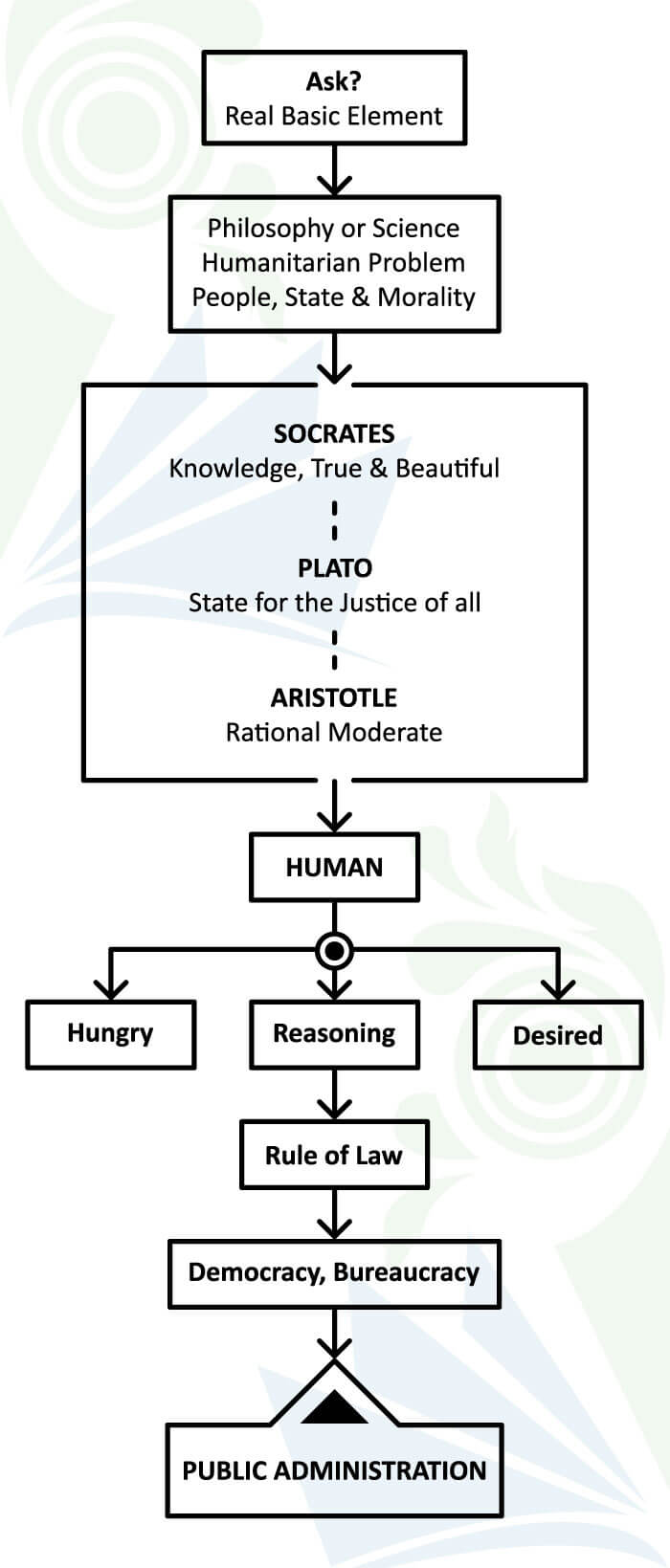
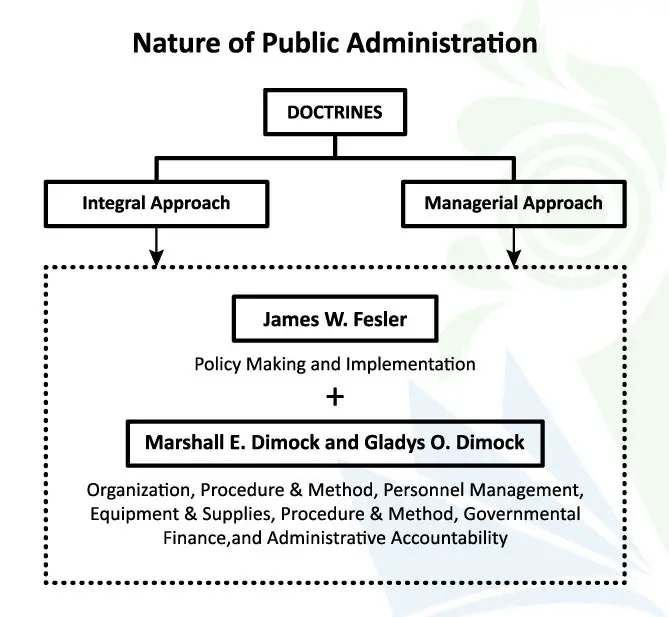

This post provides a great overview of the historical context surrounding public administration. It’s fascinating to see how Woodrow Wilson’s ideas continue to influence the field today. I particularly appreciated the discussion on how his vision for a professional civil service is still relevant in modern governance. Thank you for shedding light on this important topic!